ENIB 2022 - groupe B : Grande roue
Révision datée du 18 janvier 2022 à 19:00 par Perglaz (discussion | contributions)
Sommaire
[masquer]Equipe
- Kaddah Salah El Dine
- Malherbe Julie
- Floch Louanne
- La Marre Pierre
- Kam Kamgaing Dany Borel
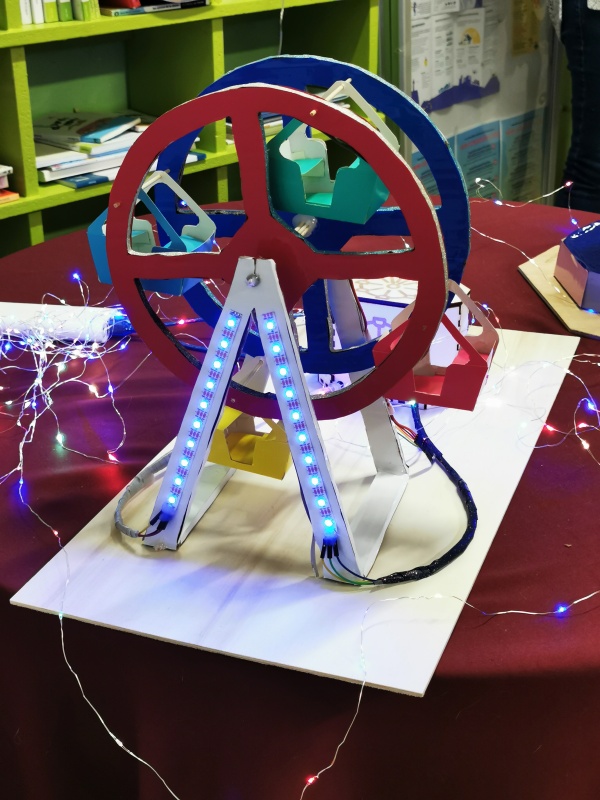
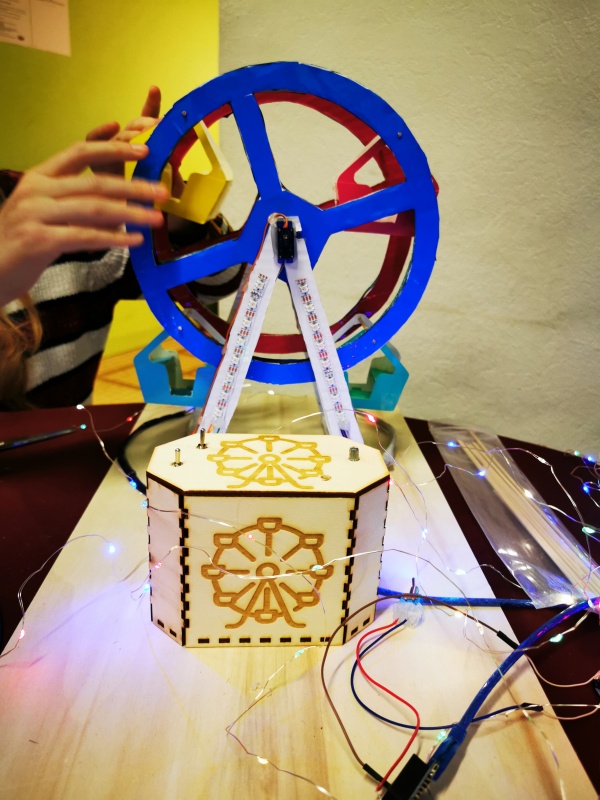
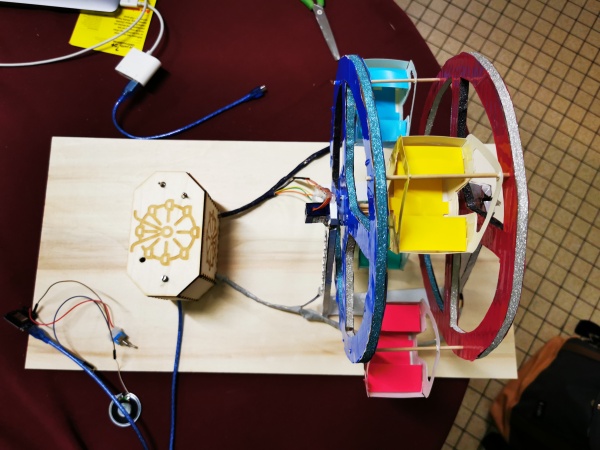
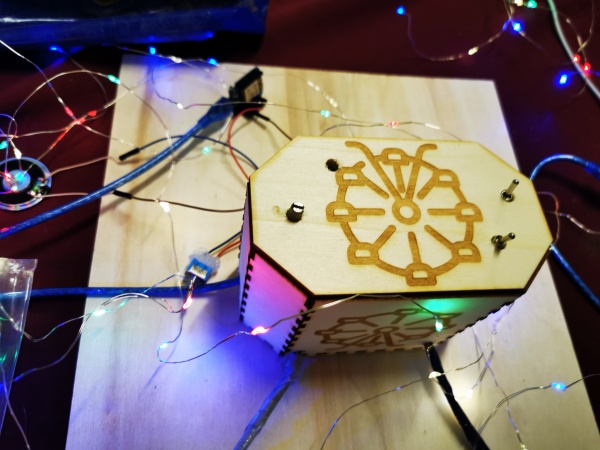
photo du projet
Que fait ce projet ?
La grande roue peut tourner dans les 2 sens, émet une musique, et est illuminée au niveau de son support
Liste des composants
Technique:
- Wemos D1 Mini x2
- servo moteur x1
- potentiomètre x1
- bandeau de led rvb adressable WS2812B x36 led
- Haut parleur x1
- interrupteur x2
- buzzer
Autre:
- carton
- papiers de couleur (blanc, bleu, rose)
- pics de bois
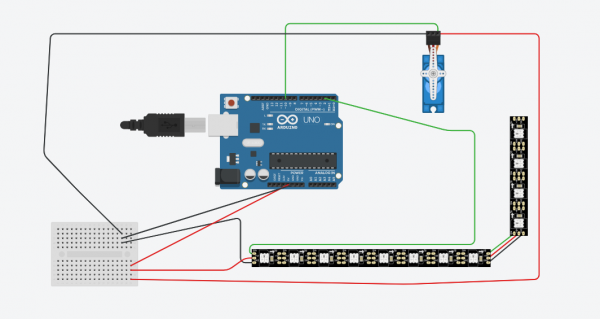
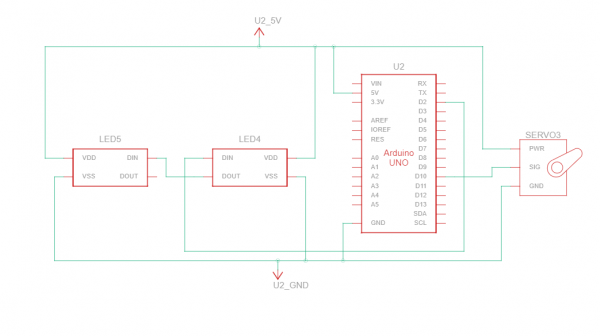
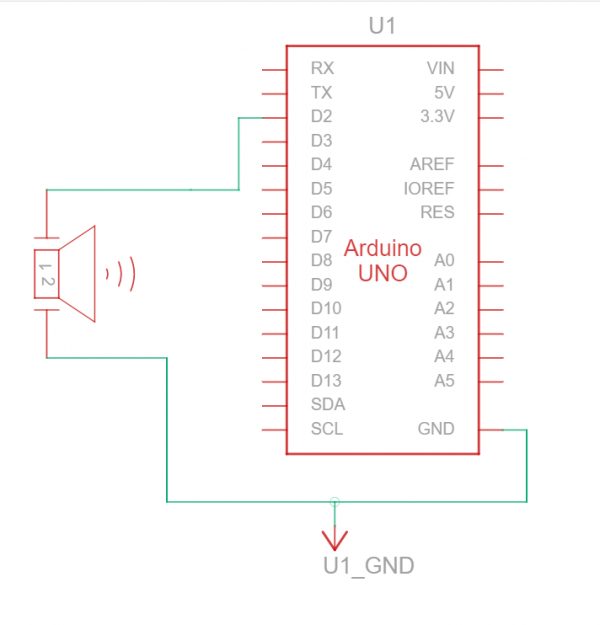
Circuit
- Roue:
- Musique:
Code
- Moteur et leds
#include <Servo.h>
#include<FastLED.h>
#define LED_PIN 5
#define NUM_LEDS 10
#define BRIGHTNESS 64
#define LED_TYPE WS2811
#define COLOR_ORDER GRB
CRGB leds[NUM_LEDS];
#define UPDATES_PER_SECOND 100
CRGBPalette16 currentPalette;
TBlendType currentBlending;
extern CRGBPalette16 myRedWhiteBluePalette;
extern const TProgmemPalette16 myRedWhiteBluePalette_p PROGMEM;
Servo esc; // create servo object to control a servo
int val; // variable to read value from analog pin
void setup()
{
esc.attach(D7); // attaches servo on D7 to the servo object
delay( 3000 ); // power-up safety delay
FastLED.addLeds<LED_TYPE, LED_PIN, COLOR_ORDER>(leds, NUM_LEDS).setCorrection( TypicalLEDStrip );
FastLED.setBrightness( BRIGHTNESS );
currentPalette = RainbowColors_p;
currentBlending = LINEARBLEND;
}
void loop()
{
val = analogRead(0); // reads potentiometer value (between 0 and 1023)
val = map(val, 0, 1023, 0, 180); // scale it to use it with the servo (between 0 and 180)
esc.write(val); // sets servo position according to scaled value
delay(15); // waits for servo to get there
ChangePalettePeriodically();
static uint8_t startIndex = 0;
startIndex = startIndex + 1; /* motion speed */
FillLEDsFromPaletteColors( startIndex);
FastLED.show();
FastLED.delay(1000 / UPDATES_PER_SECOND);
}
void FillLEDsFromPaletteColors( uint8_t colorIndex)
{
uint8_t brightness = 255;
for ( int i = 0; i < NUM_LEDS; i++) {
leds[i] = ColorFromPalette( currentPalette, colorIndex, brightness, currentBlending);
colorIndex += 3;
}
}
// There are several different palettes of colors demonstrated here.
//
// FastLED provides several 'preset' palettes: RainbowColors_p, RainbowStripeColors_p,
// OceanColors_p, CloudColors_p, LavaColors_p, ForestColors_p, and PartyColors_p.
//
// Additionally, you can manually define your own color palettes, or you can write
// code that creates color palettes on the fly. All are shown here.
void ChangePalettePeriodically()
{
uint8_t secondHand = (millis() / 1000) % 60;
static uint8_t lastSecond = 99;
if ( lastSecond != secondHand) {
lastSecond = secondHand;
if ( secondHand == 0) {
currentPalette = RainbowColors_p;
currentBlending = LINEARBLEND;
}
if ( secondHand == 10) {
currentPalette = RainbowStripeColors_p;
currentBlending = NOBLEND;
}
if ( secondHand == 15) {
currentPalette = RainbowStripeColors_p;
currentBlending = LINEARBLEND;
}
if ( secondHand == 20) {
SetupPurpleAndGreenPalette();
currentBlending = LINEARBLEND;
}
if ( secondHand == 25) {
SetupTotallyRandomPalette();
currentBlending = LINEARBLEND;
}
if ( secondHand == 30) {
SetupBlackAndWhiteStripedPalette();
currentBlending = NOBLEND;
}
if ( secondHand == 35) {
SetupBlackAndWhiteStripedPalette();
currentBlending = LINEARBLEND;
}
if ( secondHand == 40) {
currentPalette = CloudColors_p;
currentBlending = LINEARBLEND;
}
if ( secondHand == 45) {
currentPalette = PartyColors_p;
currentBlending = LINEARBLEND;
}
if ( secondHand == 50) {
currentPalette = myRedWhiteBluePalette_p;
currentBlending = NOBLEND;
}
if ( secondHand == 55) {
currentPalette = myRedWhiteBluePalette_p;
currentBlending = LINEARBLEND;
}
}
}
// This function fills the palette with totally random colors.
void SetupTotallyRandomPalette()
{
for ( int i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
currentPalette[i] = CHSV( random8(), 255, random8());
}
}
// This function sets up a palette of black and white stripes,
// using code. Since the palette is effectively an array of
// sixteen CRGB colors, the various fill_* functions can be used
// to set them up.
void SetupBlackAndWhiteStripedPalette()
{
// 'black out' all 16 palette entries...
fill_solid( currentPalette, 16, CRGB::Black);
// and set every fourth one to white.
currentPalette[0] = CRGB::White;
currentPalette[4] = CRGB::White;
currentPalette[8] = CRGB::White;
currentPalette[12] = CRGB::White;
}
// This function sets up a palette of purple and green stripes.
void SetupPurpleAndGreenPalette()
{
CRGB purple = CHSV( HUE_PURPLE, 255, 255);
CRGB green = CHSV( HUE_GREEN, 255, 255);
CRGB black = CRGB::Black;
currentPalette = CRGBPalette16(
green, green, black, black,
purple, purple, black, black,
green, green, black, black,
purple, purple, black, black );
}
// This example shows how to set up a static color palette
// which is stored in PROGMEM (flash), which is almost always more
// plentiful than RAM. A static PROGMEM palette like this
// takes up 64 bytes of flash.
const TProgmemPalette16 myRedWhiteBluePalette_p PROGMEM =
{
CRGB::Red,
CRGB::Gray, // 'white' is too bright compared to red and blue
CRGB::Blue,
CRGB::Black,
CRGB::Red,
CRGB::Gray,
CRGB::Blue,
CRGB::Black,
CRGB::Red,
CRGB::Red,
CRGB::Gray,
CRGB::Gray,
CRGB::Blue,
CRGB::Blue,
CRGB::Black,
CRGB::Black
};
- Musique:
/*
Song of storms - Legend of Zelda
Connect a piezo buzzer or speaker to pin 11 or select a new pin.
More songs available at https://github.com/robsoncouto/arduino-songs
Robson Couto, 2019
*/
#define NOTE_B0 31
#define NOTE_C1 33
#define NOTE_CS1 35
#define NOTE_D1 37
#define NOTE_DS1 39
#define NOTE_E1 41
#define NOTE_F1 44
#define NOTE_FS1 46
#define NOTE_G1 49
#define NOTE_GS1 52
#define NOTE_A1 55
#define NOTE_AS1 58
#define NOTE_B1 62
#define NOTE_C2 65
#define NOTE_CS2 69
#define NOTE_D2 73
#define NOTE_DS2 78
#define NOTE_E2 82
#define NOTE_F2 87
#define NOTE_FS2 93
#define NOTE_G2 98
#define NOTE_GS2 104
#define NOTE_A2 110
#define NOTE_AS2 117
#define NOTE_B2 123
#define NOTE_C3 131
#define NOTE_CS3 139
#define NOTE_D3 147
#define NOTE_DS3 156
#define NOTE_E3 165
#define NOTE_F3 175
#define NOTE_FS3 185
#define NOTE_G3 196
#define NOTE_GS3 208
#define NOTE_A3 220
#define NOTE_AS3 233
#define NOTE_B3 247
#define NOTE_C4 262
#define NOTE_CS4 277
#define NOTE_D4 294
#define NOTE_DS4 311
#define NOTE_E4 330
#define NOTE_F4 349
#define NOTE_FS4 370
#define NOTE_G4 392
#define NOTE_GS4 415
#define NOTE_A4 440
#define NOTE_AS4 466
#define NOTE_B4 494
#define NOTE_C5 523
#define NOTE_CS5 554
#define NOTE_D5 587
#define NOTE_DS5 622
#define NOTE_E5 659
#define NOTE_F5 698
#define NOTE_FS5 740
#define NOTE_G5 784
#define NOTE_GS5 831
#define NOTE_A5 880
#define NOTE_AS5 932
#define NOTE_B5 988
#define NOTE_C6 1047
#define NOTE_CS6 1109
#define NOTE_D6 1175
#define NOTE_DS6 1245
#define NOTE_E6 1319
#define NOTE_F6 1397
#define NOTE_FS6 1480
#define NOTE_G6 1568
#define NOTE_GS6 1661
#define NOTE_A6 1760
#define NOTE_AS6 1865
#define NOTE_B6 1976
#define NOTE_C7 2093
#define NOTE_CS7 2217
#define NOTE_D7 2349
#define NOTE_DS7 2489
#define NOTE_E7 2637
#define NOTE_F7 2794
#define NOTE_FS7 2960
#define NOTE_G7 3136
#define NOTE_GS7 3322
#define NOTE_A7 3520
#define NOTE_AS7 3729
#define NOTE_B7 3951
#define NOTE_C8 4186
#define NOTE_CS8 4435
#define NOTE_D8 4699
#define NOTE_DS8 4978
#define REST 0
// change this to make the song slower or faster
int tempo = 150;//108 originalement
// change this to whichever pin you want to use
int buzzer = D2;
// notes of the moledy followed by the duration.
// a 4 means a quarter note, 8 an eighteenth , 16 sixteenth, so on
// !!negative numbers are used to represent dotted notes,
// so -4 means a dotted quarter note, that is, a quarter plus an eighteenth!!
int melody[] = {
// Song of storms - The Legend of Zelda Ocarina of Time.
// Score available at https://musescore.com/user/4957541/scores/1545401
NOTE_D4,4, NOTE_A4,4, NOTE_A4,4,
REST,8, NOTE_E4,8, NOTE_B4,2,
NOTE_F4,4, NOTE_C5,4, NOTE_C5,4,
REST,8, NOTE_E4,8, NOTE_B4,2,
NOTE_D4,4, NOTE_A4,4, NOTE_A4,4,
REST,8, NOTE_E4,8, NOTE_B4,2,
NOTE_F4,4, NOTE_C5,4, NOTE_C5,4,
REST,8, NOTE_E4,8, NOTE_B4,2,
NOTE_D4,8, NOTE_F4,8, NOTE_D5,2,
NOTE_D4,8, NOTE_F4,8, NOTE_D5,2,
NOTE_E5,-4, NOTE_F5,8, NOTE_E5,8, NOTE_E5,8,
NOTE_E5,8, NOTE_C5,8, NOTE_A4,2,
NOTE_A4,4, NOTE_D4,4, NOTE_F4,8, NOTE_G4,8,
NOTE_A4,-2,
NOTE_A4,4, NOTE_D4,4, NOTE_F4,8, NOTE_G4,8,
NOTE_E4,-2,
NOTE_D4,8, NOTE_F4,8, NOTE_D5,2,
NOTE_D4,8, NOTE_F4,8, NOTE_D5,2,
NOTE_E5,-4, NOTE_F5,8, NOTE_E5,8, NOTE_E5,8,
NOTE_E5,8, NOTE_C5,8, NOTE_A4,2,
NOTE_A4,4, NOTE_D4,4, NOTE_F4,8, NOTE_G4,8,
NOTE_A4,2, NOTE_A4,4,
NOTE_D4,1,
};
// sizeof gives the number of bytes, each int value is composed of two bytes (16 bits)
// there are two values per note (pitch and duration), so for each note there are four bytes
int notes = sizeof(melody) / sizeof(melody[0]) / 2;
// this calculates the duration of a whole note in ms
int wholenote = (60000 * 4) / tempo;
int divider = 0, noteDuration = 0;
void setup() {
// iterate over the notes of the melody.
// Remember, the array is twice the number of notes (notes + durations)
for (int thisNote = 0; thisNote < notes * 2; thisNote = thisNote + 2) {
// calculates the duration of each note
divider = melody[thisNote + 1];
if (divider > 0) {
// regular note, just proceed
noteDuration = (wholenote) / divider;
} else if (divider < 0) {
// dotted notes are represented with negative durations!!
noteDuration = (wholenote) / abs(divider);
noteDuration *= 1.5; // increases the duration in half for dotted notes
}
// we only play the note for 90% of the duration, leaving 10% as a pause
tone(buzzer, melody[thisNote], noteDuration*0.9);
// Wait for the specief duration before playing the next note.
delay(noteDuration);
// stop the waveform generation before the next note.
noTone(buzzer);
}
}
void loop() {
// we repeat the melody
for (int thisNote = 0; thisNote < notes * 2; thisNote = thisNote + 2) {
// calculates the duration of each note
divider = melody[thisNote + 1];
if (divider > 0) {
// regular note, just proceed
noteDuration = (wholenote) / divider;
} else if (divider < 0) {
// dotted notes are represented with negative durations!!
noteDuration = (wholenote) / abs(divider);
noteDuration *= 1.5; // increases the duration in half for dotted notes
}
// we only play the note for 90% of the duration, leaving 10% as a pause
tone(buzzer, melody[thisNote], noteDuration*0.9);
// Wait for the specief duration before playing the next note.
delay(noteDuration);
// stop the waveform generation before the next note.
noTone(buzzer);
}
}
Pistes d'amélioration
- Utiliser du carton mousse au lieu de carton pour la roue
- Faire une grande roue plus grande
- cacher la partie musique dans une cabine
Sources
- créer la grande roue:
https://www.lasdi.com/la-grande-roue.html
- code servo moteur:
https://raspi.tv/2018/using-wemos-d1-mini-to-control-a-brushless-motor-with-esc-and-servo-signals
- bandeau de led rvb adressable WS2812B:
https://www.raspberryme.com/guide-pour-la-bande-led-rvb-adressable-ws2812b-avec-arduino/
- bibliothèque des leds WS2812B (le code utilise l'exemple "ColorPalette" de cette bibliothèque):
https://github.com/FastLED/FastLED/archive/master.zip
- utiliser Wemos D1 Mini avec arduino:
http://www.wikidebrouillard.org/wiki/Utiliser_le_D1_mini_avec_Arduino