ENIB 2022 - groupe D : Knossos : Différence entre versions
(→Quel est le projet ?) |
(→Liste des composants) |
||
| (10 révisions intermédiaires par le même utilisateur non affichées) | |||
| Ligne 5 : | Ligne 5 : | ||
[[Fichier:Knossos duotone.png|300px|vignette]] | [[Fichier:Knossos duotone.png|300px|vignette]] | ||
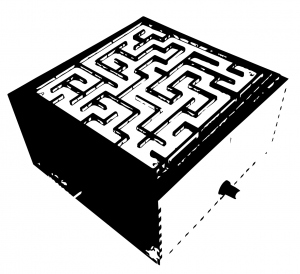
Nous avons eu l'idée de faire un labyrinthe. Le nom, Knossos, provient de l'île sur laquelle se trouvait le labyrinthe du minotaure. | Nous avons eu l'idée de faire un labyrinthe. Le nom, Knossos, provient de l'île sur laquelle se trouvait le labyrinthe du minotaure. | ||
| + | |||
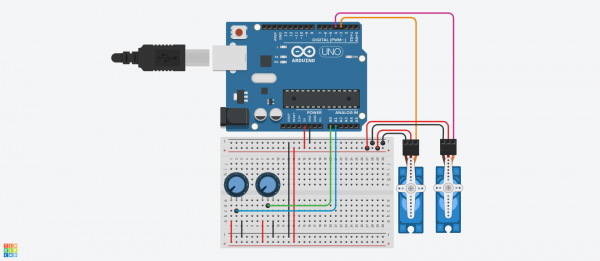
Deux servo-moteurs contrôlent les axes X et Y de la platforme. | Deux servo-moteurs contrôlent les axes X et Y de la platforme. | ||
Les mouvements sont réalisés par 2 potentiomètres. | Les mouvements sont réalisés par 2 potentiomètres. | ||
| Ligne 17 : | Ligne 18 : | ||
* Malus potentiel toutes les 30 secs (non realisé) | * Malus potentiel toutes les 30 secs (non realisé) | ||
| − | ==Liste des composants== | + | ==Liste des composants final== |
* arduino nano | * arduino nano | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
* 2 servo-moteurs SG90 | * 2 servo-moteurs SG90 | ||
* 2 potentionmètres | * 2 potentionmètres | ||
* des fils | * des fils | ||
* planche | * planche | ||
| + | * bille | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Pour améliorer === | ||
| + | * écran | ||
| + | * haut parleur 8ohms / buzzer | ||
==Sources== | ==Sources== | ||
| Ligne 42 : | Ligne 44 : | ||
#include <Servo.h> | #include <Servo.h> | ||
| − | #define P1 A0 | + | #define P1 A0 // macro Potentiometer1 -> A0 |
| − | #define P2 A1 | + | #define P2 A1 // macro Potentiometer2 -> A1 |
| − | #define S1 4 | + | #define S1 4 // macro Servo1 -> D4 |
| − | #define S2 3 | + | #define S2 3 // macro Servo2 -> D3 |
Servo Servo1; | Servo Servo1; | ||
Servo Servo2; | Servo Servo2; | ||
int val1, val2; | int val1, val2; | ||
| − | + | // le type '''long''' est un grand integer | |
long compute(long x, long in_min, long in_max, long out_min, long out_max) { | long compute(long x, long in_min, long in_max, long out_min, long out_max) { | ||
long temp = (x - in_min) * (out_max - out_min) / (in_max - in_min) + out_min; | long temp = (x - in_min) * (out_max - out_min) / (in_max - in_min) + out_min; | ||
| Ligne 59 : | Ligne 61 : | ||
void setup() { | void setup() { | ||
| − | Servo1.attach(S1); | + | Servo1.attach(S1); // Servo1 -> pin D4 |
| − | Servo2.attach(S2); | + | Servo2.attach(S2); // Servo2 -> pin D3 |
} | } | ||
void loop() { | void loop() { | ||
| − | val1 = analogRead(P1); | + | val1 = analogRead(P1); // read potentiometer1 value (between 0 and 1023) |
| − | val1 = compute(val1, 400, 700, 70, 120); | + | val1 = compute(val1, 400, 700, 70, 120); // linear reaction for value1 [400, 700] -> [70, 120] |
| − | Servo1.write(val1); | + | Servo1.write(val1); // write value1 to Servo1 |
| − | val2 = analogRead(P2); | + | val2 = analogRead(P2); // read potentiometer2 value (between 0 and 1023) |
| − | val2 = compute(val2, 400, 700, 30, 60); | + | val2 = compute(val2, 400, 700, 30, 60); // linear reaction for value2 [400, 700] -> [30, 60] |
| − | Servo2.write(val2); | + | Servo2.write(val2); // write value2 to Servo2 |
} | } | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Fichiers découpeuse laser== | ||
==Catégories== | ==Catégories== | ||
[[Catégorie:Enib2022]] | [[Catégorie:Enib2022]] | ||
Version actuelle datée du 21 janvier 2022 à 10:09
Sommaire
Photo de l'Équipe
Quel est le projet ?
Nous avons eu l'idée de faire un labyrinthe. Le nom, Knossos, provient de l'île sur laquelle se trouvait le labyrinthe du minotaure.
Deux servo-moteurs contrôlent les axes X et Y de la platforme. Les mouvements sont réalisés par 2 potentiomètres.
Partie non-réalisée: Mise en œuvre de la musique et d'un écran pour un retour visuel, avec usage de capteurs pour le début et la fin du parcours.
But du jeu
Le but du jeu est d'emmener la bille du point de départ noté D à l'arrivée 1 notée A1 puis à l'arrivée 2 notée A2.
- Solo : Il faut emmener la bille du début à la fin.
- Version co-op: Chacun son potentionmètre.
- Malus potentiel toutes les 30 secs (non realisé)
Liste des composants final
- arduino nano
- 2 servo-moteurs SG90
- 2 potentionmètres
- des fils
- planche
- bille
Pour améliorer
- écran
- haut parleur 8ohms / buzzer
Sources
Plans découpeuse laser:
- Boîte: https://www.festi.info/boxes.py/
- Labyrinthe: https://adashrod.github.io/LaserCutMazes/designer
Schémas
- Schéma final
Code
- Code final
1 #include <Servo.h>
2
3 #define P1 A0 // macro Potentiometer1 -> A0
4 #define P2 A1 // macro Potentiometer2 -> A1
5 #define S1 4 // macro Servo1 -> D4
6 #define S2 3 // macro Servo2 -> D3
7
8 Servo Servo1;
9 Servo Servo2;
10 int val1, val2;
11 // le type '''long''' est un grand integer
12 long compute(long x, long in_min, long in_max, long out_min, long out_max) {
13 long temp = (x - in_min) * (out_max - out_min) / (in_max - in_min) + out_min;
14 if (temp < out_min) return out_min;
15 if (temp > out_max) return out_max;
16 else return temp;
17 }
18
19 void setup() {
20 Servo1.attach(S1); // Servo1 -> pin D4
21 Servo2.attach(S2); // Servo2 -> pin D3
22 }
23
24 void loop() {
25 val1 = analogRead(P1); // read potentiometer1 value (between 0 and 1023)
26 val1 = compute(val1, 400, 700, 70, 120); // linear reaction for value1 [400, 700] -> [70, 120]
27 Servo1.write(val1); // write value1 to Servo1
28 val2 = analogRead(P2); // read potentiometer2 value (between 0 and 1023)
29 val2 = compute(val2, 400, 700, 30, 60); // linear reaction for value2 [400, 700] -> [30, 60]
30 Servo2.write(val2); // write value2 to Servo2
31 }