ENIB 2020 : Mimic2000 : Différence entre versions
(→Que fait ce projet ?) |
(→Que fait ce projet ?) |
||
| (23 révisions intermédiaires par le même utilisateur non affichées) | |||
| Ligne 1 : | Ligne 1 : | ||
==Qui sommes nous== | ==Qui sommes nous== | ||
| − | |||
| − | [[Fichier: | + | [[Fichier:Mimic2000_Logo.png|500px]] |
==Que fait ce projet ? == | ==Que fait ce projet ? == | ||
| − | Recréation [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mimic_(Dungeons_%26_Dragons) Mimic Chest] | + | [[Fichier:Mimic2000_D&DMimic.JPG|100px|right|thumb|Mimic Chest]] |
| + | Recréation [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mimic_(Dungeons_%26_Dragons) Mimic Chest] | ||
| − | Le Coffre est en bois et le haut du coffre est en carton | + | ''In the Dungeons & Dragons fantasy role-playing game, the mimic is a type of fictional monster. It is portrayed as being able to change its shape to disguise its body as an inanimate object, commonly a chest. The mimic has a powerful adhesive that holds fast to creatures who touch the creature, allowing the mimic to beat the creature with its powerful pseudopods. The mimic was introduced in the first edition Advanced Dungeons & Dragons game's original Monster Manual. The mimic has appeared in subsequent editions. Several variants of the creature have been introduced, with a variety of abilities and sizes.'' |
| + | |||
| + | Le Coffre est en bois et le haut du coffre est en carton. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Dans le coffre il y a un bouton rouge, si une personne appuie dessus le haut du coffre se referme sur la main de celle-ci. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Le haut du coffre s'ouvre au bout de quelques secondes. | ||
==Liste des composants== | ==Liste des composants== | ||
| + | * Résistance 10k Ohms X1 [[Fichier:Mimic2000 Résistances.JPG|100px|Résistance|thumb|Résistance de 10 kOhms|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Bouton [[Fichier:Mimic2000 Bouton.JPG|250px|Bouton|thumb|Exemple de Bouton|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Micro Servo moteur à Rotation Continue FS90R [[Fichier:Mimic2000 servo.JPG|250px|Servo|thumb|Servomoteur|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Alimentation Externe [[Fichier:Mimic2000_Alim.JPG|300px||thumb|Exemple d'une alimentation externe|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Arduino Nano [[Fichier:Mimic2000_Nano.jpg|350px|Arduino Nano|thumb|Arduino Nano|center]] | ||
| − | + | ou | |
| − | * | + | * Arduino UNO [[Fichier:Mimic2000_Uno.jpg|250px|Arduino UNO|thumb|Arduino UNO|center]] |
| − | + | ==Montage== | |
| − | + | ===Réalisation du coffre=== | |
| + | Nous avons construit notre coffre en découpant dans des planches en bois les quatre cotés du coffre ainsi que le fond. | ||
| − | + | Le haut du coffre est fait en carton afin que le servo moteur ne force pas trop. | |
| − | + | Afin de cacher la partie électronique, un double fond a été réalisé où le bouton est fixé. | |
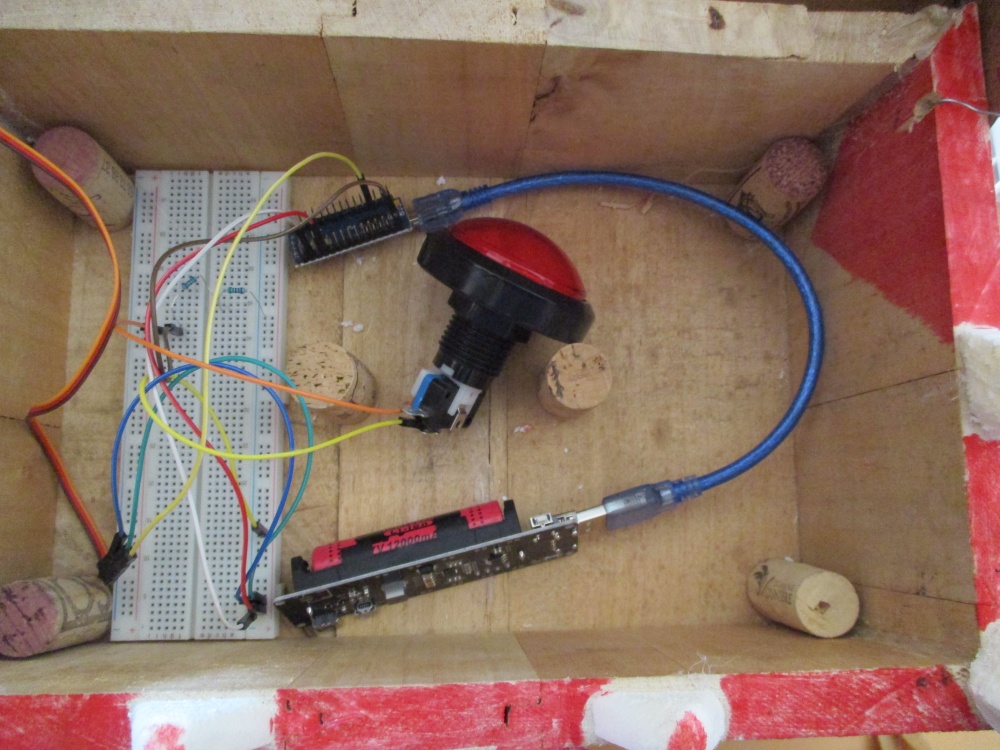
| − | + | ===Câblage électronique=== | |
| + | |||
| + | [[Fichier:Mimic2000_Cablage.JPG|1000px]] | ||
| − | + | ===Habillage=== | |
| + | [[Fichier:Mimic2000_Profil.JPG|1000px]] | ||
| + | [[Fichier:Mimic2000_Devant.JPG|1000px]] | ||
| + | [[Fichier:Mimic2000_Dessus.JPG|1000px]] | ||
==Code== | ==Code== | ||
| Ligne 32 : | Ligne 53 : | ||
int button = 13; | int button = 13; | ||
| − | int servo_control = 9; | + | int button = 13; // button pin |
| − | int pause = 1000; | + | int servo_control = 9; //servo pin |
| − | + | int pause = 1000; // delay before open chest | |
| − | + | bool open_top = false; // command to open the chest | |
| − | bool open_top = false; | + | bool close_top = false; // command to close the chest |
| − | bool close_top = false; | + | bool secure = false; // secure to desactivate the button during the closing and the opening of the chest |
| − | bool secure = false; | + | int time_open = 500; // time to open the chest |
| − | int time_open = | + | int time_close = 500; // time to close the chest |
| − | int time_close = | + | int open_sens = 0; // sens of rotation of the servo to open the chest |
| − | int open_sens = | + | int close_sens =180; //sens of rotation of the servo to close the chest |
| − | int close_sens = | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | |||
#include"Servo.h" | #include"Servo.h" | ||
#include <Servo.h> | #include <Servo.h> | ||
| − | Servo myservo; | + | Servo myservo; // create servo |
void setup() { | void setup() { | ||
// put your setup code here, to run once: | // put your setup code here, to run once: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
pinMode(button, INPUT); | pinMode(button, INPUT); | ||
| − | Serial.begin(9600); | + | Serial.begin(9600); // enable serial print |
| − | myservo.attach(servo_control); | + | myservo.attach(servo_control); // add servo |
| − | + | myservo.write(90); // stop the servo | |
| − | |||
| − | myservo.write(90); | ||
}// end of setup | }// end of setup | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
void loop() { | void loop() { | ||
// put your main code here, to run repeatedly: | // put your main code here, to run repeatedly: | ||
if (digitalRead(button) && secure == false) { | if (digitalRead(button) && secure == false) { | ||
| − | Serial.println("button is ok"); | + | Serial.println("button is ok"); // test the functionment of the button |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
open_top = true; | open_top = true; | ||
| − | secure = true; | + | secure = true; // desactivation of the button |
} | } | ||
if (open_top == true && close_top == false) {// open box | if (open_top == true && close_top == false) {// open box | ||
| − | myservo.write(open_sens); | + | myservo.write(open_sens); // order to open the chest |
| − | delay(time_open); | + | delay(time_open); // time during the open of the chest |
| − | myservo.write(90); | + | myservo.write(90); // stop the servo |
open_top = false; | open_top = false; | ||
close_top = true; | close_top = true; | ||
| Ligne 92 : | Ligne 96 : | ||
if (open_top == false && close_top == true) {// close box | if (open_top == false && close_top == true) {// close box | ||
delay(pause); | delay(pause); | ||
| − | myservo.write(close_sens); | + | myservo.write(close_sens);// order to close the chest |
| − | delay(time_close); | + | delay(time_close); // time during the close of the chest |
| − | myservo.write(90); | + | myservo.write(90); // stop the servo |
close_top = false; | close_top = false; | ||
| − | secure = false; | + | secure = false; //activation of the button |
| − | |||
| − | |||
} | } | ||
| Ligne 105 : | Ligne 107 : | ||
/* | /* | ||
Micro Servo à Rotation Continue FS90R | Micro Servo à Rotation Continue FS90R | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://boutique.semageek.com/fr/1036-micro-servo-moteur-a-rotation-continu-fs90r.html. | ||
DESCRIPTION | DESCRIPTION | ||
Version actuelle datée du 20 janvier 2020 à 15:03
Sommaire
Qui sommes nous
Que fait ce projet ?
Recréation Mimic Chest
In the Dungeons & Dragons fantasy role-playing game, the mimic is a type of fictional monster. It is portrayed as being able to change its shape to disguise its body as an inanimate object, commonly a chest. The mimic has a powerful adhesive that holds fast to creatures who touch the creature, allowing the mimic to beat the creature with its powerful pseudopods. The mimic was introduced in the first edition Advanced Dungeons & Dragons game's original Monster Manual. The mimic has appeared in subsequent editions. Several variants of the creature have been introduced, with a variety of abilities and sizes.
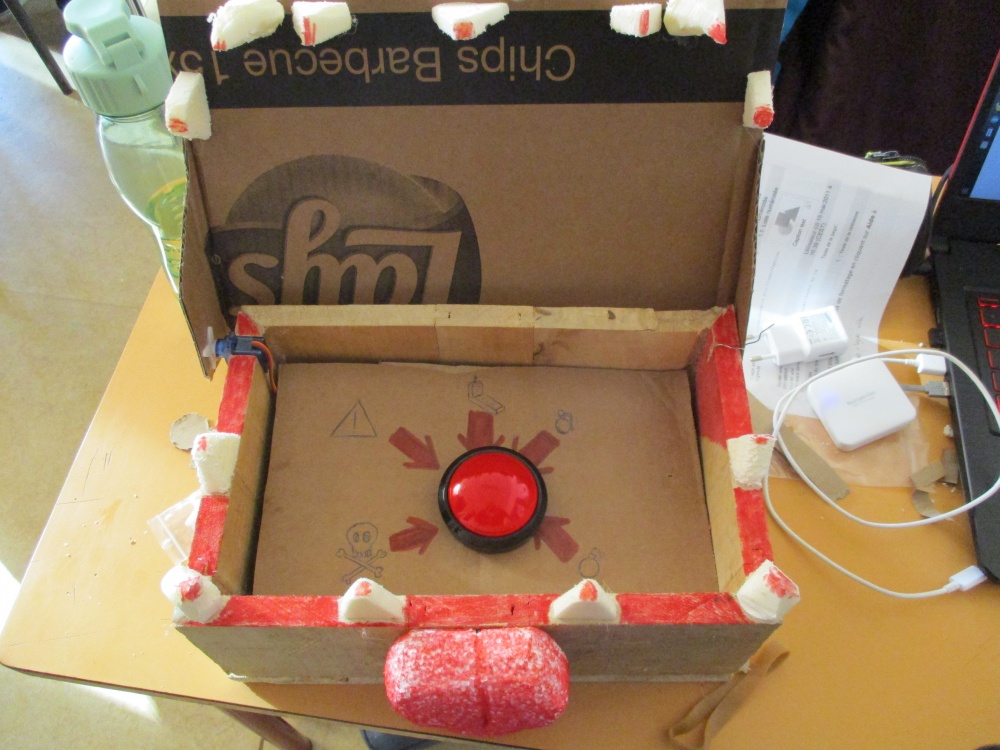
Le Coffre est en bois et le haut du coffre est en carton.
Dans le coffre il y a un bouton rouge, si une personne appuie dessus le haut du coffre se referme sur la main de celle-ci.
Le haut du coffre s'ouvre au bout de quelques secondes.
Liste des composants
- Résistance 10k Ohms X1
- Bouton
- Micro Servo moteur à Rotation Continue FS90R
- Alimentation Externe
- Arduino Nano
ou
- Arduino UNO
Montage
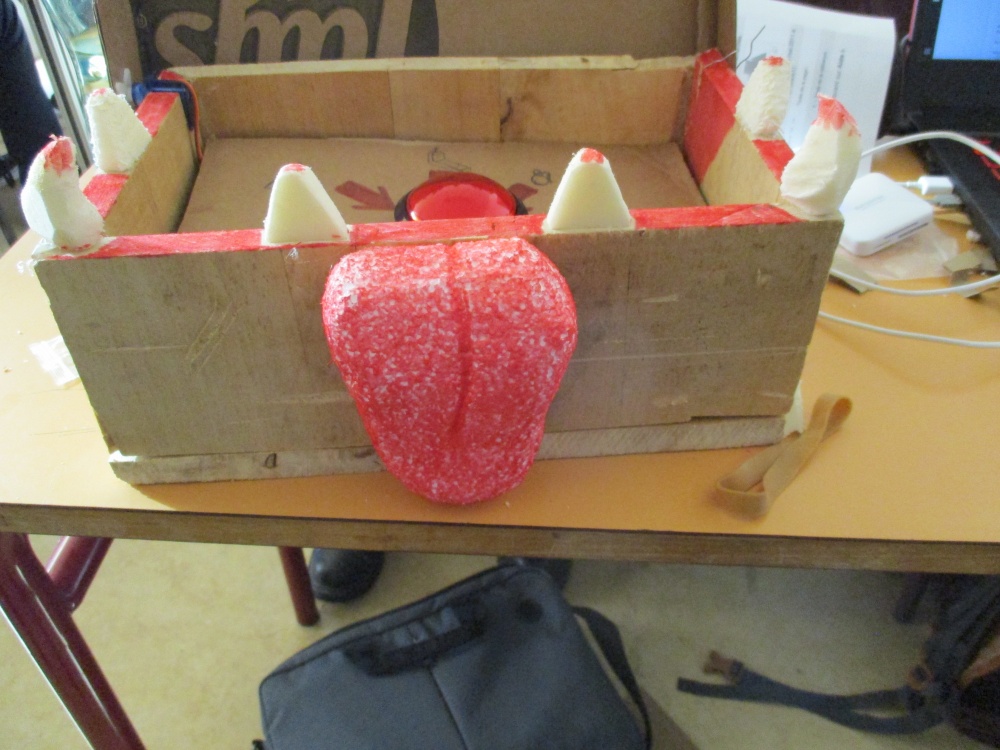
Réalisation du coffre
Nous avons construit notre coffre en découpant dans des planches en bois les quatre cotés du coffre ainsi que le fond.
Le haut du coffre est fait en carton afin que le servo moteur ne force pas trop.
Afin de cacher la partie électronique, un double fond a été réalisé où le bouton est fixé.
Câblage électronique
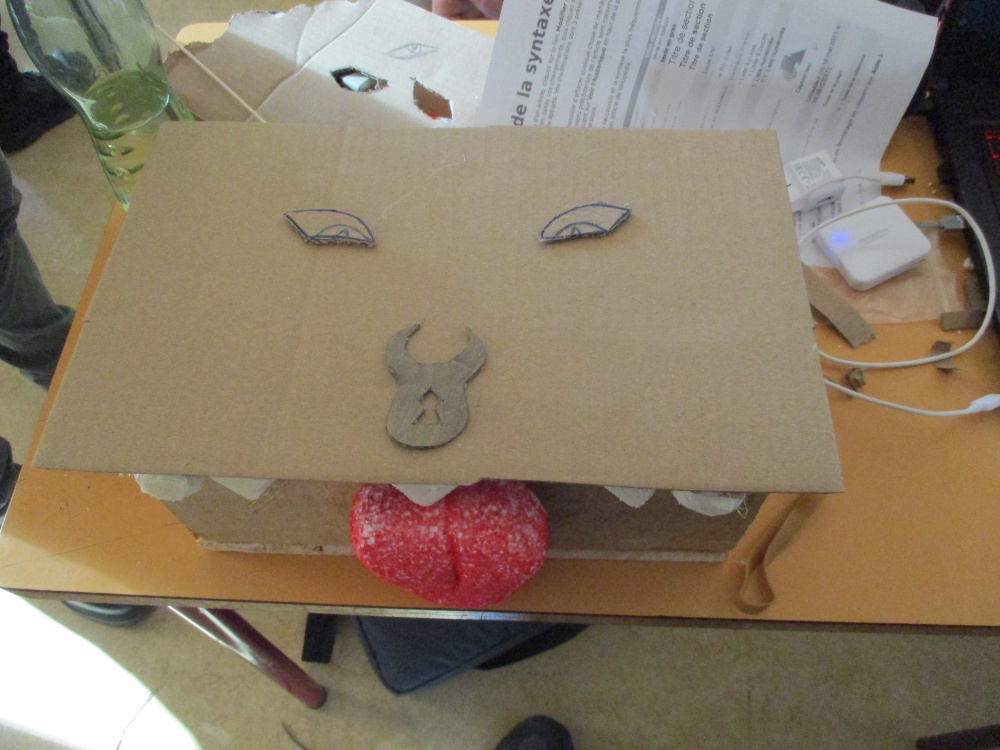
Habillage
Code
int button = 13;
int button = 13; // button pin
int servo_control = 9; //servo pin
int pause = 1000; // delay before open chest
bool open_top = false; // command to open the chest
bool close_top = false; // command to close the chest
bool secure = false; // secure to desactivate the button during the closing and the opening of the chest
int time_open = 500; // time to open the chest
int time_close = 500; // time to close the chest
int open_sens = 0; // sens of rotation of the servo to open the chest
int close_sens =180; //sens of rotation of the servo to close the chest
#include"Servo.h"
#include <Servo.h>
Servo myservo; // create servo
void setup() {
// put your setup code here, to run once:
pinMode(button, INPUT);
Serial.begin(9600); // enable serial print
myservo.attach(servo_control); // add servo
myservo.write(90); // stop the servo
}// end of setup
void loop() {
// put your main code here, to run repeatedly:
if (digitalRead(button) && secure == false) {
Serial.println("button is ok"); // test the functionment of the button
open_top = true;
secure = true; // desactivation of the button
}
if (open_top == true && close_top == false) {// open box
myservo.write(open_sens); // order to open the chest
delay(time_open); // time during the open of the chest
myservo.write(90); // stop the servo
open_top = false;
close_top = true;
}
if (open_top == false && close_top == true) {// close box
delay(pause);
myservo.write(close_sens);// order to close the chest
delay(time_close); // time during the close of the chest
myservo.write(90); // stop the servo
close_top = false;
secure = false; //activation of the button
}
}// end of loop
/*
Micro Servo à Rotation Continue FS90R
https://boutique.semageek.com/fr/1036-micro-servo-moteur-a-rotation-continu-fs90r.html.
DESCRIPTION
Ce servo tourne à 360 degrés vers l'avant ou vers l'arrière au lieu de bouger d'une position à une autre comme un servo classique (servo à rotation continue).
Vous pouvez utiliser n'importe quel code, hardware ou librairie dédiés à des servos pour le contrôler.
C'est le servo idéal pour faire des robots mobiles simples. Il est livré avec quatre palonniers et vis de fixation.
Pour contrôler ce servo avec un Arduino, nous vous conseillons de connecter le fil de signal sur les pins 9 ou 10 et d'utiliser la librairie "servo" inclue dans Arduino IDE (voir liens ci-dessous).
La position "90" correspond à la position "stop" (impulsions de 1500µs), la position "180" correspond à la vitesse max en avant (impulsions de 2000µs)
et la position "0" correspond à la vitesse max en arrière (impulsions de 1000µs).
Ce servo peut avoir besoin d'une calibration. Il suffit pour cela de choisir la position "90" ou "stop" et d'ajuster le potentiomètre situé proche de la sortie
du câble jusqu'à ce que le servo soit immobile (le boîtier du servo est perçé à cet endroit pour y avoir facilement accès).
*/