Voiture télécommandée par bluetooth : Différence entre versions
(→Modélisation du châssis) |
|||
| (2 révisions intermédiaires par le même utilisateur non affichées) | |||
| Ligne 1 : | Ligne 1 : | ||
==Description du projet== | ==Description du projet== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Il s'agit de réaliser une voiture télécommandée avec une carte Arduino, la télécommande étant un téléphone Android en communication via bluetooth avec un module Bluetooth lié a la carte Arduino. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Chaque roue arrière sera alimentée par un des moteurs. En faisant tourner un des moteurs plus vite que l'autre, la voiture pourra ainsi tourner. | ||
| + | Pour piloter la carte de puissance, nous utiliserons une carte Arduino Uno qui avec un code adapté permettra de distribué la puissante exact pour faire tourner la voiture dans le meme sens qu'indique l'analogue. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Une carte de puissance a pour but de distribuer de la puissance, à la dose souhaitée, à des composants électriques, dans notre cas deux moteurs. | ||
| + | La carte de puissance est donc alimentée par une source d'énergie et la carte Arduino pilote cette carte afin de décider : | ||
| + | de la puissance a distribué au moteur, ce qui permettra de le faire tourner plus ou moins vite (notion de PWM) | ||
==Matériel== | ==Matériel== | ||
| Ligne 129 : | Ligne 138 : | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
===Modélisation du châssis=== | ===Modélisation du châssis=== | ||
| − | [[Fichier:Image_3.png | 700px | thumb | center | | + | [[Fichier:Image_3.png | 700px | thumb | center | châssis]] |
| − | === | + | |
| + | ===Images=== | ||
[[Fichier:Image 1.jpg | 700px | thumb | center | Image 1]] | [[Fichier:Image 1.jpg | 700px | thumb | center | Image 1]] | ||
[[Fichier:Image 2.jpg | 700px | thumb | center | Image 2]] | [[Fichier:Image 2.jpg | 700px | thumb | center | Image 2]] | ||
| Ligne 138 : | Ligne 148 : | ||
Ahmed EL Boukri | Ahmed EL Boukri | ||
Assaad EL Fellah Idrissi | Assaad EL Fellah Idrissi | ||
| + | [[Catégorie:enib2019]] | ||
Version actuelle datée du 22 janvier 2019 à 11:09
Sommaire
Description du projet
Il s'agit de réaliser une voiture télécommandée avec une carte Arduino, la télécommande étant un téléphone Android en communication via bluetooth avec un module Bluetooth lié a la carte Arduino.
Chaque roue arrière sera alimentée par un des moteurs. En faisant tourner un des moteurs plus vite que l'autre, la voiture pourra ainsi tourner. Pour piloter la carte de puissance, nous utiliserons une carte Arduino Uno qui avec un code adapté permettra de distribué la puissante exact pour faire tourner la voiture dans le meme sens qu'indique l'analogue.
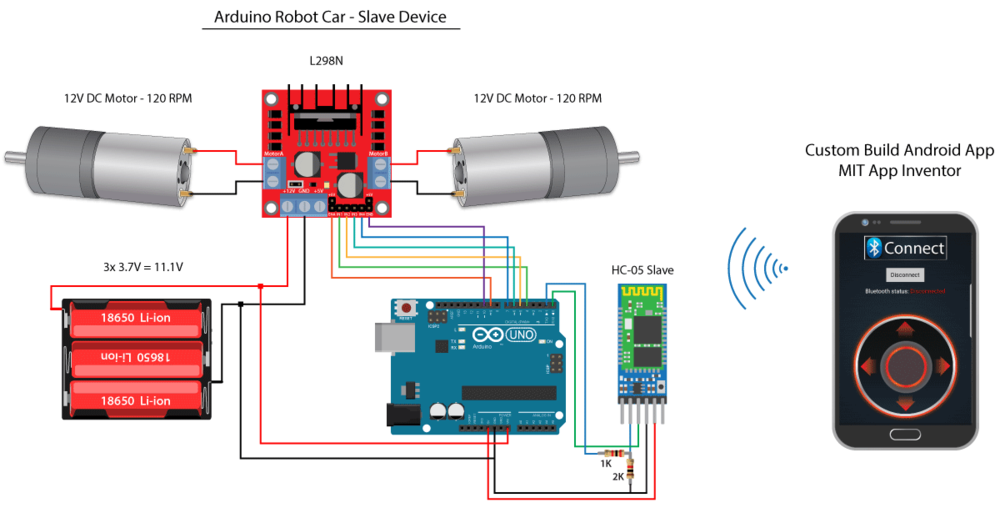
Une carte de puissance a pour but de distribuer de la puissance, à la dose souhaitée, à des composants électriques, dans notre cas deux moteurs. La carte de puissance est donc alimentée par une source d'énergie et la carte Arduino pilote cette carte afin de décider : de la puissance a distribué au moteur, ce qui permettra de le faire tourner plus ou moins vite (notion de PWM)
Matériel
• module Bluetooth HC-06 • Variateur de vitesse L298N • 2x moteurs • Arduino Uno • 6x piles 1.5 V • Câbles
Réalisation
Schéma de câblage
Code Arduino
#define enA 9
#define in1 4
#define in2 5
#define enB 10
#define in3 6
#define in4 7
int xAxis, yAxis;
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
int motorSpeedA = 0;
int motorSpeedB = 0;
void setup() {
pinMode(enA, OUTPUT);
pinMode(enB, OUTPUT);
pinMode(in1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(in2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(in3, OUTPUT);
pinMode(in4, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(38400); // Default communication rate of the Bluetooth module
}
void loop() {
// Default value - no movement when the Joystick stays in the center
xAxis = 510;
yAxis = 510;
// Read the incoming data from the Smartphone Android App
while (Serial.available() >= 2) {
x = Serial.read();
delay(10);
y = Serial.read();
}
delay(10);
// Makes sure we receive corrent values
if (x > 60 & x < 220) {
xAxis = map(x, 220, 60, 1023, 0); // Convert the smartphone X and Y values to 0 - 1023 range, suitable motor for the motor control code below
}
if (y > 60 & y < 220) {
yAxis = map(y, 220, 60, 0, 1023);
}
// Y-axis used for forward and backward control
if (yAxis < 470) {
// Set Motor A backward
digitalWrite(in1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(in2, LOW);
// Set Motor B backward
digitalWrite(in3, HIGH);
digitalWrite(in4, LOW);
// Convert the declining Y-axis readings for going backward from 470 to 0 into 0 to 255 value for the PWM signal for increasing the motor speed
motorSpeedA = map(yAxis, 470, 0, 0, 255);
motorSpeedB = map(yAxis, 470, 0, 0, 255);
}
else if (yAxis > 550) {
// Set Motor A forward
digitalWrite(in1, LOW);
digitalWrite(in2, HIGH);
// Set Motor B forward
digitalWrite(in3, LOW);
digitalWrite(in4, HIGH);
// Convert the increasing Y-axis readings for going forward from 550 to 1023 into 0 to 255 value for the PWM signal for increasing the motor speed
motorSpeedA = map(yAxis, 550, 1023, 0, 255);
motorSpeedB = map(yAxis, 550, 1023, 0, 255);
}
// If joystick stays in middle the motors are not moving
else {
motorSpeedA = 0;
motorSpeedB = 0;
}
// X-axis used for left and right control
if (xAxis < 470) {
// Convert the declining X-axis readings from 470 to 0 into increasing 0 to 255 value
int xMapped = map(xAxis, 470, 0, 0, 255);
// Move to left - decrease left motor speed, increase right motor speed
motorSpeedA = motorSpeedA - xMapped;
motorSpeedB = motorSpeedB + xMapped;
// Confine the range from 0 to 255
if (motorSpeedA < 0) {
motorSpeedA = 0;
}
if (motorSpeedB > 255) {
motorSpeedB = 255;
}
}
if (xAxis > 550) {
// Convert the increasing X-axis readings from 550 to 1023 into 0 to 255 value
int xMapped = map(xAxis, 550, 1023, 0, 255);
// Move right - decrease right motor speed, increase left motor speed
motorSpeedA = motorSpeedA + xMapped;
motorSpeedB = motorSpeedB - xMapped;
// Confine the range from 0 to 255
if (motorSpeedA > 255) {
motorSpeedA = 255;
}
if (motorSpeedB < 0) {
motorSpeedB = 0;
}
}
// Prevent buzzing at low speeds (Adjust according to your motors. My motors couldn't start moving if PWM value was below value of 70)
if (motorSpeedA < 70) {
motorSpeedA = 0;
}
if (motorSpeedB < 70) {
motorSpeedB = 0;
}
analogWrite(enA, motorSpeedA); // Send PWM signal to motor A
analogWrite(enB, motorSpeedB); // Send PWM signal to motor B
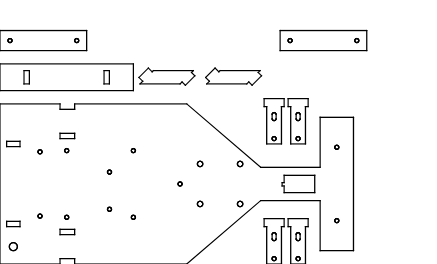
Modélisation du châssis
Images
Équipe
Zakaria Chellaoui Toufik EL Guerch Ahmed EL Boukri Assaad EL Fellah Idrissi