Voiture télécommandée par bluetooth : Différence entre versions
(→Modélisation du châssis) |
|||
| Ligne 131 : | Ligne 131 : | ||
[[Fichier:Image_3.jpg | 700px | thumb | center | châssis ]] | [[Fichier:Image_3.jpg | 700px | thumb | center | châssis ]] | ||
| + | ===Modélisation du châssis=== | ||
| + | [[Fichier:Image_3.png | 700px | thumb | center | Image 1]] | ||
===truc=== | ===truc=== | ||
[[Fichier:Image 1.jpg | 700px | thumb | center | Image 1]] | [[Fichier:Image 1.jpg | 700px | thumb | center | Image 1]] | ||
Version du 21 janvier 2019 à 22:53
Sommaire
Description du projet
Matériel
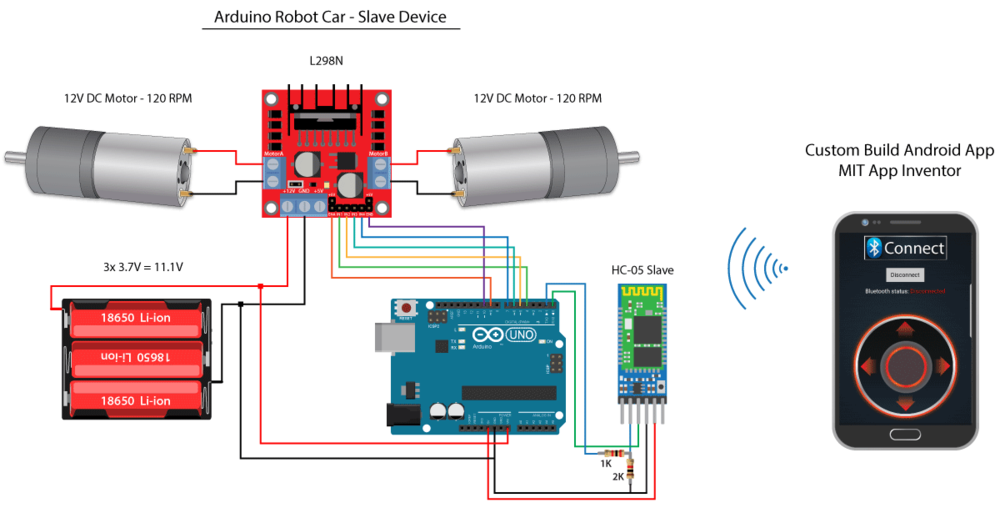
• module Bluetooth HC-06 • Variateur de vitesse L298N • 2x moteurs • Arduino Uno • 6x piles 1.5 V • Câbles
Réalisation
Schéma de câblage
Code Arduino
#define enA 9
#define in1 4
#define in2 5
#define enB 10
#define in3 6
#define in4 7
int xAxis, yAxis;
int x = 0;
int y = 0;
int motorSpeedA = 0;
int motorSpeedB = 0;
void setup() {
pinMode(enA, OUTPUT);
pinMode(enB, OUTPUT);
pinMode(in1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(in2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(in3, OUTPUT);
pinMode(in4, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(38400); // Default communication rate of the Bluetooth module
}
void loop() {
// Default value - no movement when the Joystick stays in the center
xAxis = 510;
yAxis = 510;
// Read the incoming data from the Smartphone Android App
while (Serial.available() >= 2) {
x = Serial.read();
delay(10);
y = Serial.read();
}
delay(10);
// Makes sure we receive corrent values
if (x > 60 & x < 220) {
xAxis = map(x, 220, 60, 1023, 0); // Convert the smartphone X and Y values to 0 - 1023 range, suitable motor for the motor control code below
}
if (y > 60 & y < 220) {
yAxis = map(y, 220, 60, 0, 1023);
}
// Y-axis used for forward and backward control
if (yAxis < 470) {
// Set Motor A backward
digitalWrite(in1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(in2, LOW);
// Set Motor B backward
digitalWrite(in3, HIGH);
digitalWrite(in4, LOW);
// Convert the declining Y-axis readings for going backward from 470 to 0 into 0 to 255 value for the PWM signal for increasing the motor speed
motorSpeedA = map(yAxis, 470, 0, 0, 255);
motorSpeedB = map(yAxis, 470, 0, 0, 255);
}
else if (yAxis > 550) {
// Set Motor A forward
digitalWrite(in1, LOW);
digitalWrite(in2, HIGH);
// Set Motor B forward
digitalWrite(in3, LOW);
digitalWrite(in4, HIGH);
// Convert the increasing Y-axis readings for going forward from 550 to 1023 into 0 to 255 value for the PWM signal for increasing the motor speed
motorSpeedA = map(yAxis, 550, 1023, 0, 255);
motorSpeedB = map(yAxis, 550, 1023, 0, 255);
}
// If joystick stays in middle the motors are not moving
else {
motorSpeedA = 0;
motorSpeedB = 0;
}
// X-axis used for left and right control
if (xAxis < 470) {
// Convert the declining X-axis readings from 470 to 0 into increasing 0 to 255 value
int xMapped = map(xAxis, 470, 0, 0, 255);
// Move to left - decrease left motor speed, increase right motor speed
motorSpeedA = motorSpeedA - xMapped;
motorSpeedB = motorSpeedB + xMapped;
// Confine the range from 0 to 255
if (motorSpeedA < 0) {
motorSpeedA = 0;
}
if (motorSpeedB > 255) {
motorSpeedB = 255;
}
}
if (xAxis > 550) {
// Convert the increasing X-axis readings from 550 to 1023 into 0 to 255 value
int xMapped = map(xAxis, 550, 1023, 0, 255);
// Move right - decrease right motor speed, increase left motor speed
motorSpeedA = motorSpeedA + xMapped;
motorSpeedB = motorSpeedB - xMapped;
// Confine the range from 0 to 255
if (motorSpeedA > 255) {
motorSpeedA = 255;
}
if (motorSpeedB < 0) {
motorSpeedB = 0;
}
}
// Prevent buzzing at low speeds (Adjust according to your motors. My motors couldn't start moving if PWM value was below value of 70)
if (motorSpeedA < 70) {
motorSpeedA = 0;
}
if (motorSpeedB < 70) {
motorSpeedB = 0;
}
analogWrite(enA, motorSpeedA); // Send PWM signal to motor A
analogWrite(enB, motorSpeedB); // Send PWM signal to motor B
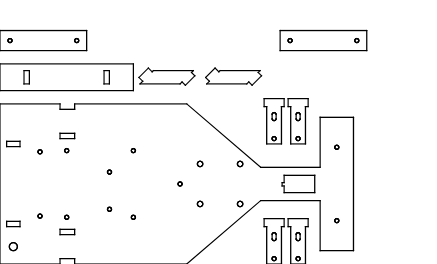
Modélisation du châssis
Modélisation du châssis
truc
Équipe
Zakaria Chellaoui Toufik EL Guerch Ahmed EL Boukri Assaad EL Fellah Idrissi